| Cascade DataHub™ : Version 6.4 | ||
|---|---|---|
 | Chapter 3. Making Connections |  |
Table of Contents
We generally use one of three of DDE commands to connect to the Cascade DataHub: DDEPoke, DDERequest, or DDEAdvise.
If you plan to use DDEPoke or DDERequest, the DataHub will act as a DDE server. You will have to set up your DDE-enabled program to send commands to the DataHub. The following table summarizes the setup.
| DDE Command | Program action | Program setup | Data flow | DataHub action | DataHub setup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDERequest | Reads data from DataHub | Configuration, macro, or code | <== | Acts as a server | DDE service name |
| DDEPoke | Writes data to DataHub | Configuration, macro, or code | ==> | Acts as a server | DDE service name |
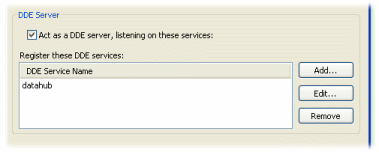
The Cascade DataHub is preconfigured to act as a DDE server. You can double-check this as follows:
 .
.
You will probably need to configure your communicating program to read or write data. As you may know, DDE defines data using three variables: service, topic, and item, as follows:
A name used by a DDE server to identify its service to DDE clients, such as datahub for the DataHub, or excel for Excel.
A way to categorize items. This corresponds to a Cascade DataHub data domain.
A variable that holds a value. This corresponds to a Cascade DataHub point.
Different DDE clients use the service, topic, and item names in different ways. For example, Excel uses them in the formula for a cell, like this:
=service|topic!item
For a service named datahub, and a point named test_point in the default data domain the Excel formula would look like this:
=datahub|default!test_point
Client programs that accept drag and drop values can be configured from the DataHub Data Browser window. It offers several formats from a drop-down list:
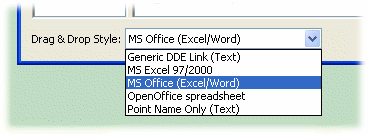
If none of these formats suits your purpose, you might be able to drag in the points and then modify the results. Otherwise, simply enter the service name, topic, and item in the way that the client program allows.
You can use DDEAdvise commands to set up automatically-updating data streams to and from the DataHub. To do so, you will first need to determine the direction of data flow. The program that sends data acts as a server, and has a DDE service name. The program that receives the data acts as a client. The following table summarizes the connections.
| DDE Command | Program action | Program setup | Data flow | DataHub action | DataHub setup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDEAdvise | Acts as client | Set up a DDE connection | <== | Acts as server | DDE service name |
| DDEAdvise | Acts as server | DDE service name | ==> | Acts as client | Add DDE connection item(s) |
If the data is flowing from the DataHub, you need to configure it as a DDE server (above). Otherwise, you should configure it as a DDE client.
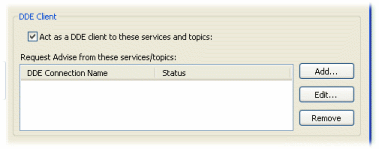
To set up the DataHub for your program to receive data via DDEAdvise, you need to ensure that the DataHub is acting as a DDE client, and then add an Advise loop for each point you plan to send data for. Here's how:
 .
.
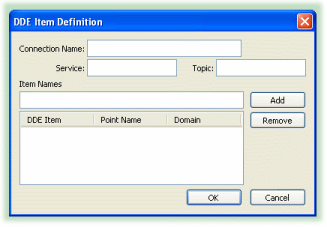
Connection Name: choose a name to identify this connection. It must be unique among all connection names.
Service: type in the service name.
![[Note]](images/note.gif) | If you don't know the service name or topic name for your program, check your user's manual. Also, there is a list of commonly used service names in the DDE Overview appendix. |
Topic: type in the name of your topic.
Item Names: type the name of the item you wish to add.
![[Note]](images/note.gif) | Check the name in the Data Domain column. If it is not what you need, double-click it to select it, and change it. |
The DataHub is now ready to act as a DDE client.
Copyright © 1995-2010 by Cogent Real-Time Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.